Learning how to generate line charts with AI opens new horizons in data visualization, enabling the creation of dynamic, accurate, and visually appealing graphs with minimal effort. This approach leverages advanced algorithms to analyze datasets, identify patterns, and render insightful visual representations that enhance understanding across various industries.
By integrating AI tools and platforms, users can streamline the process of designing, customizing, and optimizing line charts. From data preparation to interactive features, this guide explores essential techniques and best practices to harness AI’s potential for producing compelling visual analytics tailored to diverse needs.
Overview of Line Charts with AI
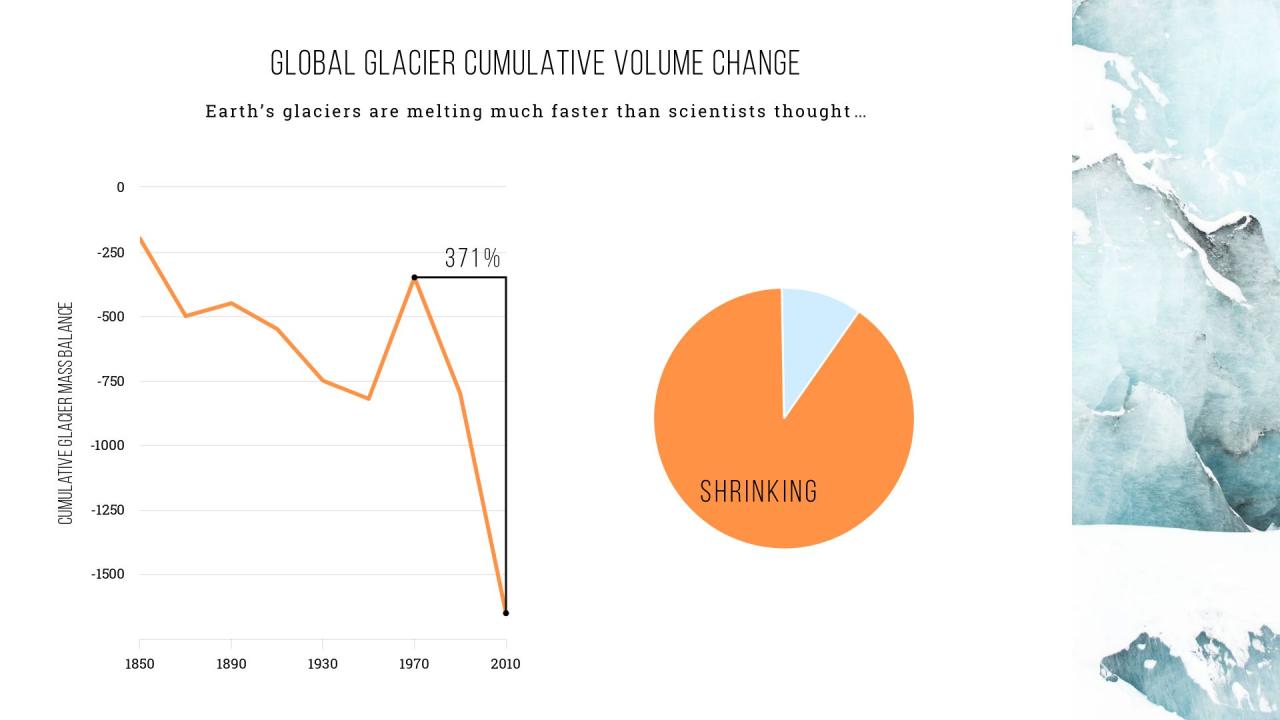
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into the process of creating line charts revolutionizes traditional data visualization by enabling the generation of highly accurate, dynamic, and insightful visual representations of data trends. AI-powered tools analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and automatically produce line charts that reflect real-time changes and complex relationships without manual intervention. This integration not only accelerates the visualization process but also enhances precision, making it an invaluable asset across various sectors.
Utilizing AI for line chart creation offers numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, adaptability to large and complex datasets, and improved accuracy in trend analysis. Unlike manual chart generation, AI systems can quickly process data from multiple sources, clean and organize it, and generate clear visualizations that highlight critical insights. This capability is particularly advantageous in environments where rapid decision-making is essential, such as financial markets, healthcare analytics, and operational monitoring.
Common Applications of AI-Generated Line Charts in Various Industries
AI-driven line charts are increasingly employed across diverse industries to facilitate data-driven decision-making and strategic planning. They serve as vital tools in sectors where tracking changes over time is crucial for operational success or strategic insights.
| Industry | Application of AI-Generated Line Charts |
|---|---|
| Finance | Real-time stock price analysis, investment trend monitoring, and risk assessment. AI models can forecast future stock movements based on historical data, visualized through dynamic line charts for traders and analysts. |
| Healthcare | Monitoring patient health metrics, disease progression, and the effectiveness of treatments. AI helps visualize complex health data over time, aiding clinicians in making informed decisions quickly. |
| Marketing | Tracking campaign performance, customer engagement trends, and sales growth. Automated line charts enable marketing teams to adjust strategies based on real-time insights. |
| Manufacturing | Process optimization by analyzing production metrics, equipment performance, and quality control data. AI-generated line charts help identify inefficiencies and predict maintenance needs before breakdowns occur. |
| Energy | Monitoring power consumption, renewable energy outputs, and grid stability over time. AI assists in forecasting energy demands and optimizing resource distribution through visualized trends. |
In each of these applications, AI enhances the ability to interpret complex datasets rapidly and accurately, empowering professionals to make more informed, timely decisions. The fusion of AI and line chart visualization stands as a testament to the evolving landscape of data analytics, where automation and precision drive innovation across industries.
Tools and Platforms for AI-Driven Line Chart Generation
As artificial intelligence continues to revolutionize data visualization, various tools and platforms have emerged to facilitate the effortless creation of accurate and aesthetically appealing line charts. These solutions leverage advanced algorithms to automate data processing, enhance customization, and simplify integration with existing workflows. Understanding the landscape of AI-enabled charting tools is essential for users aiming to optimize their data storytelling and analysis capabilities.
Many contemporary platforms combine machine learning, natural language processing, and automation to deliver dynamic charting experiences. They cater to a broad spectrum of users, from data analysts and business professionals to educators and researchers. By comparing the features, capabilities, and integration options of these tools, users can select the most suitable platform to meet their specific visualization needs, streamline workflows, and improve decision-making processes.
Popular Software and Platforms for AI-Driven Line Chart Generation
The following list highlights some of the most widely adopted AI-powered charting tools that facilitate automatic line chart creation, customization, and analysis:
- Tableau with Einstein Analytics: Combines Tableau’s robust data visualization capabilities with Salesforce’s Einstein AI to enable predictive analytics and automated chart generation, including line charts that adapt to data trends.
- Microsoft Power BI with AI Insights: Integrates AI features such as natural language queries and automated insights, allowing users to generate and customize line charts directly from textual descriptions or data patterns.
- Google Data Studio with AI Extensions: Supports integrations with AI services like BigQuery ML, enabling predictive modeling that can inform and enhance line chart visualizations.
- Qlik Sense with AI Integration: Offers associative data indexing and AI-driven suggestions for creating insightful line charts, supporting complex data relationships and trend detection.
- Charticulator and Power BI Visuals: Open-source tools that utilize AI algorithms and customizable templates to generate detailed line charts, especially useful for bespoke visualizations in complex datasets.
Comparison of Features and Capabilities of AI Charting Tools
Comparing these platforms offers insights into their unique strengths and limitations, helping users identify the optimal solution based on their requirements. Key aspects to consider include automation level, customization options, ease of integration, and advanced analytical features.
| Feature | Tableau with Einstein Analytics | Microsoft Power BI with AI Insights | Google Data Studio with AI Extensions | Qlik Sense | Charticulator & Power BI Visuals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automation | High: Automates data prep and visualization suggestions | Moderate: Auto insights and natural language queries | Basic: Limited AI-driven automation, relies on integrations | High: AI-assisted trend detection and suggestions | Variable: User-driven with templates and AI algorithms |
| Customization | Extensive: Drag-and-drop, custom calculations, and scripting | Moderate: Custom visuals and scripting support | Limited: Designed for quick reports, less tailored customization | Moderate: Custom visual development and scripting | High: Fully customizable visual templates and scripting |
| Integration | Seamless: Connects with Salesforce, SQL, and cloud platforms | Seamless: Works with Azure, Office 365, and external APIs | Moderate: Integrates with Google Cloud services and APIs | Seamless: Connects with multiple data sources and APIs | Flexible: Compatible with Power BI and other visualization tools |
| Analytical Capabilities | Predictive modeling, trend analysis | Forecasting, anomaly detection, natural language processing | Basic insights with some predictive features | Pattern recognition, predictive analytics | Trend detection, custom statistical analysis |
Integrating AI with Existing Data Visualization Software
Enhancing existing data visualization workflows with AI capabilities requires strategic integration. Most AI-driven tools offer APIs, plugins, or SDKs that facilitate seamless connection to popular platforms like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio. This integration enables users to leverage AI features such as automated data cleaning, trend prediction, and natural language query processing within their familiar visualization environments.
For instance, integrating AI into Power BI can be achieved through custom visual plugins or by connecting to Azure Cognitive Services, providing capabilities like sentiment analysis or image recognition that can influence line chart insights. Similarly, Tableau can incorporate AI models developed in Python or R via scripting extensions, allowing for predictive analytics directly within visualizations. Implementing these integrations often involves configuring data pipelines, setting up APIs, and ensuring data security protocols are in place to maintain integrity and compliance.
Data Preparation for AI-Generated Line Charts
Effective data preparation is a fundamental step in ensuring that AI algorithms can generate accurate and insightful line charts. Proper cleansing, organization, and structuring of datasets directly influence the quality and interpretability of the visualizations produced. This process involves meticulously refining raw data to enhance compatibility with AI models and facilitating meaningful analysis.
Preparing data for AI-driven line chart generation requires a systematic approach that emphasizes clarity, consistency, and precision. This includes removing errors, handling missing values, and organizing data into formats that are easily processed by AI systems. Additionally, clear labeling and thoughtful annotation of data points are crucial to maintain accuracy and enhance the interpretability of the resulting charts.
Methods for Cleansing and Organizing Datasets
Before feeding datasets into an AI model, it is essential to perform comprehensive data cleansing to eliminate inaccuracies and inconsistencies. This process ensures that the AI receives high-quality input, which directly impacts the reliability of the generated line charts. The key methods include:
- Removing duplicates: Identifying and deleting repeated entries prevents skewed analysis. For instance, in sales data, duplicate records of the same transaction can distort trend visualization.
- Handling missing data: Filling gaps through interpolation, forward-fill, or backward-fill techniques ensures continuity in datasets. For example, filling missing monthly temperature readings helps maintain consistent trend lines.
- Correcting errors: Detecting and fixing data entry errors, such as incorrect date formats or outlier values, improves accuracy. Automated validation scripts can flag suspicious entries for review.
- Normalizing data: Scaling variables to a common range, such as 0-1, ensures that different data units do not bias the analysis, especially when combining multiple metrics like revenue and customer counts.
Organizing data involves structuring datasets in a logical, accessible manner. This can include categorizing data by time periods, regions, or product types, and ensuring consistent units of measurement across all entries. Such organization facilitates seamless processing by AI systems and supports meaningful visualization outcomes.
Structuring Data Tables in HTML for Optimal Processing
Presenting data in well-structured HTML tables enhances both human readability and AI processing efficiency. Responsive table designs with up to four columns allow for clear visualization of key data points while accommodating various device screens. Proper structuring allows AI algorithms to parse and interpret datasets accurately.
| Time Period | Data Series A | Data Series B | Annotations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 2024 | 150 | 200 | Peak sales observed |
| Q2 2024 | 180 | 220 | Steady growth trend |
This structured format ensures that each row represents a specific time interval, with columns clearly indicating different data series and relevant annotations. The use of responsive design techniques, like flexible widths and media queries, ensures accessibility across devices, making the data ready for AI processing.
Best Practices for Labeling and Annotating Data
Clear labeling and annotation are vital for accurate interpretation and visualization. Labels should be descriptive and standardized to avoid ambiguity, enabling AI systems to recognize and differentiate data categories effectively. Annotations add context, highlight significant points, and facilitate better understanding for users.
- Consistent labeling: Use uniform terminology for data categories, such as “Revenue” or “Customer Count,” across datasets to prevent confusion.
- Descriptive axis labels: Clearly specify units and timeframes, e.g., “Sales (USD)” or “Quarter.”
- Annotations for key points: Mark significant data points like peaks, troughs, or anomalies with brief descriptions or symbols. For example, an asterisk (*) can denote an outlier, accompanied by a tooltip or caption.
- Metadata documentation: Embedding notes about data collection methods, sources, and updates enhances transparency and accuracy.
Proper labeling and annotation ensure that AI-generated line charts are not only visually accurate but also contextually meaningful, greatly improving their utility for decision-making.
Designing Effective Line Charts with AI
Creating visually impactful and informative line charts is essential for accurate data communication. Leveraging AI in the design process empowers users to select optimal chart types, styles, and customizations that enhance readability and interpretability. By integrating AI-driven tools, data analysts and designers can streamline the process of crafting line charts that convey insights clearly and effectively, tailored to the specific needs of their audience.
Effective design with AI involves not only choosing the appropriate visual structure but also fine-tuning details such as axes, labels, and color schemes. These elements significantly influence how quickly viewers can grasp patterns and trends within the data. Utilizing AI for this purpose ensures that chart aesthetics align with best practices, reducing cognitive load and increasing the overall impact of the visualization.
Selecting Chart Types and Styles Using AI Tools
AI-powered visualization tools offer intelligent recommendations for chart types and styles based on the data characteristics and the intended analytical focus. When working with line charts, AI algorithms analyze data patterns—such as trends, fluctuations, and data density—to suggest suitable variations, including smooth lines, stepped lines, or multiple overlapping series. These tools often incorporate machine learning models trained on vast datasets to provide style suggestions that align with industry standards and user preferences.
Many platforms, like Tableau, Power BI, or specialized AI visualization solutions, enable users to input raw data and receive automated suggestions for chart configurations. This process simplifies decision-making, especially for users who may lack extensive design experience, and ensures the chosen style effectively highlights key insights.
Customizing Axes, Labels, and Colors for Improved Readability
Refining axes, labels, and colors is vital for enhancing the clarity and accessibility of line charts. AI-driven customization tools analyze data ranges and distribution to automatically set optimal axis scales, avoiding cluttered or misleading visuals. They also suggest descriptive labels and annotations that contextualize data points, making the chart more self-.
“Effective use of color can guide viewers’ attention, differentiate data series, and improve overall comprehension.”
AI facilitates intelligent color palette selection, ensuring contrast and color-blind friendliness. It can also recommend label placements and font sizes that adapt responsively across different devices and screen sizes, maintaining readability regardless of display context. These enhancements help in creating line charts that are not only visually appealing but also easy to interpret, facilitating better decision-making.
Responsive Line Chart Container Examples
To ensure broad accessibility and seamless integration into various digital environments, line charts should be embedded within responsive containers. Below are examples of HTML snippets demonstrating flexible, multi-column layouts suitable for displaying up to four charts side by side, adapting to screen sizes dynamically.
<div style="display: flex; flex-wrap: wrap; gap: 16px;">
<div style="flex: 1 1 25%; min-width: 200px;">
<div style="border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 10px;">
<canvas id="chart1" style="width: 100%; height: auto;"></canvas>
</div>
</div>
<div style="flex: 1 1 25%; min-width: 200px;">
<div style="border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 10px;">
<canvas id="chart2" style="width: 100%; height: auto;"></canvas>
</div>
</div>
<div style="flex: 1 1 25%; min-width: 200px;">
<div style="border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 10px;">
<canvas id="chart3" style="width: 100%; height: auto;"></canvas>
</div>
</div>
<div style="flex: 1 1 25%; min-width: 200px;">
<div style="border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 10px;">
<canvas id="chart4" style="width: 100%; height: auto;"></canvas>
</div>
</div>
</div>
This responsive layout ensures that each chart container adjusts seamlessly across various devices, maintaining readability and visual balance. Developers can easily embed these structures within dashboards or reports, providing users with a flexible and engaging data exploration experience.
Generating Line Charts with AI Algorithms
Transforming raw data into insightful visualizations can be significantly streamlined through the use of AI algorithms. These sophisticated models automate the process of analyzing data patterns and producing aesthetically pleasing, accurate line charts. Understanding the steps involved in leveraging AI for this purpose ensures that users can efficiently generate high-quality visualizations tailored to their specific datasets and analytical needs.
AI-driven line chart generation involves a systematic workflow that begins with data input, proceeds through parameter configuration, and concludes with the rendering of the final chart. The process leverages advanced algorithms capable of identifying trends, smoothing out noise, and optimizing line trajectories for clarity and interpretability. This approach not only accelerates chart creation but also enhances the accuracy and visual appeal of the resulting graphics.
Input Data and Configuration of AI Parameters
Effective AI-generated line charts depend heavily on the quality of input data and the meticulous configuration of algorithm parameters. The data should be comprehensive, correctly formatted, and relevant to the insights sought. Typically, datasets are imported from CSV files, spreadsheets, or direct database connections, ensuring that each data point aligns with the intended axes of the chart.
Configuring AI parameters involves setting options such as the smoothing factor, trend detection sensitivity, and interpolation methods. These parameters influence how the AI analyzes data patterns and produces the line trajectories. For instance, selecting a higher smoothing factor can help in visualizing long-term trends by reducing short-term fluctuations, while a lower sensitivity may be preferred for detecting rapid changes in data.
“Proper parameter tuning enables the AI to balance between overfitting noisy data and underfitting by oversimplifying trends, resulting in more meaningful line visualizations.”
Methods for AI to Analyze Data Patterns and Produce Smooth Line Trajectories
AI algorithms employ various statistical and machine learning techniques to analyze data patterns and generate smooth line trajectories. These methods are designed to identify underlying trends while filtering out anomalies or random fluctuations. Some commonly used techniques include:
- Moving Averages: Calculating averages over specific windows to smooth data points and reveal long-term patterns.
- Spline Interpolation: Using piecewise polynomial functions to create smooth curves that pass through or near data points, ensuring continuity and smoothness.
- Gaussian Smoothing: Applying kernel functions to reduce high-frequency noise, resulting in cleaner trend lines.
- Regression Models: Employing linear or nonlinear regression to fit data points with predictive functions, enabling visualization of trends with confidence intervals.
- Neural Networks: Leveraging deep learning models to learn complex data patterns, especially useful for large datasets with non-linear relationships.
By combining these techniques, AI can generate line charts that accurately reflect the data’s underlying trends while maintaining visual smoothness, thereby improving interpretability and decision-making.
Sample Workflow for AI-Driven Line Chart Generation
Implementing AI algorithms for line chart creation involves a structured workflow that integrates data input, processing, and visualization. This streamlined process ensures consistency and efficiency in delivering insightful visualizations.
- Data Collection and Preparation: Gather data from relevant sources, ensure it is clean, formatted correctly, and free from inconsistencies. For example, financial datasets with date and closing price columns are prepared for analysis.
- Data Input into AI System: Import the prepared dataset into the AI platform or tool, ensuring proper mapping of data columns to the chart axes.
- Parameter Configuration: Set algorithm parameters such as smoothing intensity, trend detection sensitivity, and interpolation method based on the nature of the data and visualization goals.
- AI Processing: Run the AI algorithm, which analyzes data patterns, detects trends, and generates a smooth trajectory. For example, a neural network might be trained on historical sales data to predict future trends.
- Chart Rendering: Once processing is complete, the AI system renders the line chart, incorporating visual enhancements like color coding, labels, and annotations to improve clarity.
- Review and Refinement: Examine the generated chart for accuracy and visual appeal. Adjust parameters if necessary and rerun the process to refine the visualization.
This workflow ensures that AI-driven line charts are both data-driven and visually effective, facilitating better insights and communication of complex data patterns.
Enhancing Line Charts with AI Features
Incorporating advanced AI functionalities into line charts significantly elevates their interpretability, interactivity, and overall utility. These enhancements enable users to engage more deeply with data, uncover insights effortlessly, and customize visualizations to suit specific analytical needs. By integrating AI-powered features, line charts become dynamic tools capable of adapting to diverse datasets and user interactions.
AI-driven enhancements facilitate real-time data exploration, automate complex analytical tasks, and provide intuitive interfaces that cater to both novice and expert users. This synergy between AI and data visualization not only improves decision-making processes but also streamlines the creation and interpretation of complex datasets, making data-driven insights more accessible and actionable.
Incorporating Interactive Elements and Tooltips
Interactive features such as tooltips, clickable data points, and zoom functionalities transform static line charts into interactive dashboards. These elements allow users to hover over specific points to view detailed information without cluttering the visualization. AI algorithms can further enhance these interactions by personalizing the information displayed based on user behavior or data context.
AI can analyze user interactions to predict what additional data might interest them, dynamically adjusting tooltips to highlight relevant trends or anomalies. This creates a more engaging and informative experience, enabling users to explore complex datasets with ease and precision.
Responsive tooltips adapt in real-time, providing contextual insights tailored to user interactions and data patterns.
Suggesting Optimal Data Points and Trend Lines
AI algorithms excel at identifying significant data points, such as peaks, troughs, or outliers, and suggesting these as key highlights within the chart. Additionally, AI can recommend the most appropriate trend lines—linear, polynomial, or more complex models—that accurately represent the underlying data patterns. These suggestions ensure that visualizations are not only accurate but also insightful.
By continuously analyzing incoming data, AI-driven systems can update trend lines and highlight relevant data points dynamically, ensuring the visualization remains relevant and precise. This feature is particularly valuable for real-time data monitoring, where trends can shift rapidly, such as in financial markets or network performance tracking.
Auto-scaling axes and trend line suggestions by AI enhance clarity and focus, emphasizing key insights while maintaining visual balance.
AI-Powered Enhancements Examples
Implementing AI features in line charts offers a range of benefits that streamline data interpretation and improve user engagement. Here are some examples of AI-powered enhancements:
- Responsive tooltips: Dynamic information boxes that adapt based on user interaction and data context, providing detailed insights without overwhelming the viewer.
- Auto-scaling axes: AI-driven adjustment of axis ranges to ensure that all significant data points are visible and the chart maintains optimal readability even as data updates occur.
- Dynamic updating: Real-time modification of the chart to reflect new data, trends, or user preferences, enabling continuous data exploration without manual intervention.
These enhancements leverage AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets rapidly, predict user needs, and adapt visualizations on the fly, thereby making line charts more interactive, insightful, and user-friendly.
Troubleshooting and Optimization
Achieving accurate and visually effective AI-generated line charts requires addressing common issues that may arise during the generation process. Optimizing both data input and AI configurations ensures the clarity, reliability, and interpretability of the charts. Validating AI outputs against raw data is essential to confirm that visual representations accurately reflect underlying information, thereby enhancing trust and decision-making efficacy.
Common Issues in AI-Generated Line Charts and Solutions
Identifying typical problems encountered during automated line chart creation allows for targeted interventions, minimizing inaccuracies and improving visual quality. These issues often stem from data inconsistencies, misconfigured algorithms, or limitations within the AI tools used.
| Issue | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Data Mapping | Misalignment of data points causing inaccurate lines or distortions. | Ensure proper data labeling and verify data mappings within AI configurations; pre-process data to match expected formats. |
| Overlapping Lines or Cluttered Charts | Multiple data series overlapping, reducing clarity. | Use distinct colors, line styles, or annotations; filter or aggregate data to simplify visual complexity. |
| Inconsistent Scales | Disparate axes scales distort comparisons. | Normalize data or set consistent axis ranges; verify axis configurations before generation. |
| Missing Data Points | Gaps in data lead to broken lines. | Impute missing data using interpolation techniques or clean datasets prior to input. |
| Unintended Chart Artifacts | Artificial lines or artifacts due to AI misinterpretation. | Refine AI parameters, increase training data if applicable, or manually review outputs for correction. |
Methods to Optimize Data Input and AI Configurations for Clarity
Proper data preparation and configuration tuning are fundamental to generating clear and meaningful line charts. Optimizing these aspects minimizes misinterpretations and enhances visual insights.
- Data Cleaning and Standardization: Remove or correct anomalies, ensure consistent units, and align data formats to reduce noise and ambiguity.
- Feature Selection: Include only relevant variables to prevent clutter and focus analysis on key trends.
- Scaling and Normalization: Apply techniques such as min-max scaling or z-score normalization to ensure comparability across datasets.
- Parameter Tuning: Adjust AI model parameters, like learning rate or number of iterations, to improve output stability and accuracy.
- Input Validation: Use validation datasets to verify data integrity before feeding into AI systems, reducing errors and improving chart quality.
Note: Regularly revisiting and refining data input strategies enhances AI performance, leading to more precise and visually effective line charts.
Validating AI Outputs Against Raw Data
Ensuring that AI-generated line charts accurately reflect the underlying data is crucial for maintaining credibility and enabling informed decision-making. Validation involves systematic comparison and analysis of visual outputs with raw data sources.
Implementing validation procedures helps detect discrepancies, errors, or misrepresentations resulting from AI processing. It involves cross-checking plotted data points, trend lines, and annotations against original datasets.
| Validation Technique | Description | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Overlay Comparison | Superimpose raw data points onto the AI-generated chart for visual inspection. | Use transparent overlays or side-by-side charts to identify deviations or inaccuracies. |
| Statistical Checks | Calculate summary statistics (mean, median, variance) from raw data and compare with derived metrics from the chart. | Ensure that trends, peaks, and troughs in the visual align with calculated values. |
| Data Point Sampling | Select random data points from raw data and verify their placement within the generated chart. | Use these samples to confirm the fidelity of the AI rendering, especially in critical data regions. |
| Automated Validation Scripts | Develop scripts to extract data from AI outputs and compare directly with raw datasets. | Implement threshold-based checks to flag significant discrepancies for manual review. |
By systematically validating AI-generated graphs against raw data, analysts can identify inaccuracies promptly, refine AI configurations, and ensure the final visualizations serve as reliable representations of the underlying information.
Best Practices for Publishing AI-Generated Line Charts
Effective publication of AI-generated line charts involves careful consideration of embedding techniques, layout responsiveness, and accessibility features. Implementing these best practices ensures that visualizations are both visually appealing and universally accessible across diverse audiences and devices.
Adhering to structured guidelines for embedding charts within web pages enhances user experience, maintains design consistency, and promotes clarity. Proper layout structuring and accessibility considerations further ensure that all users, including those with disabilities, can interpret and interact with the visual data effectively.
Embedding Line Charts into Websites Using HTML Tables
Embedding AI-generated line charts into websites often involves integrating visualizations within HTML structures such as tables. Tables provide a straightforward method to organize multiple charts or accompanying data in a grid-like format, facilitating a clean and organized presentation.
When embedding charts within HTML tables, consider the following guidelines:
- Assign descriptive
altoraria-labelattributes to image-based charts to improve accessibility for screen readers. - Use
<caption>tags within the<table>element to provide context about the chart’s data or purpose. - Ensure that each table cell (
<td>) containing a chart is appropriately sized and aligned for optimal visibility across devices. - Maintain semantic clarity by pairing each chart with relevant textual descriptions or data summaries below or beside the visualization.
Structuring Charts within Responsive Layouts Using <table> Tags with Up to 4 Columns
Designing responsive layouts is crucial for ensuring that line charts display correctly on various screen sizes, from desktops to mobile devices. Using <table> tags with a maximum of four columns allows for flexible, grid-based arrangements that adapt well to different viewports.
Implementing such layouts involves:
- Defining a
<table>element with CSS styles that enable responsiveness, such as percentage-based widths and flexible cell sizing. - Dividing the table into
<tr>(table row) elements, each containing up to four<td>(table data) cells. - Embedding individual charts within each
<td>, ensuring that images or interactive visualizations scale correctly using CSS properties likemax-width: 100%; height: auto;. - Using media queries to adjust the number of columns dynamically, such as reducing from four to two or one column on smaller screens for improved readability.
This approach guarantees that charts are displayed in an organized manner without cluttering the interface, regardless of device constraints.
Accessibility Considerations for AI-Created Visualizations
Making AI-generated line charts accessible is essential for inclusive data communication. Accessibility features enhance understanding for users with visual impairments, cognitive differences, or those relying on assistive technologies.
Key considerations include:
- Descriptive Alternative Text: Provide comprehensive
alttext that summarizes the chart’s key insights, trends, and data points. For example, “Line chart showing the increase in sales from Q1 to Q4, with a peak in October.” - Semantic Annotations: Use ARIA labels and roles to clarify the purpose of the visualization, such as
role="img"andaria-labelledbyreferencing descriptive headings. - Accessible Data Tables: When data is presented alongside the chart, ensure tables are properly structured with headers and summaries, enabling screen readers to interpret data effectively.
- Color Contrast and Patterns: Use high-contrast color schemes and distinguishable line patterns to aid users with color vision deficiencies.
- Keyboard Navigation: If charts are interactive, ensure they can be navigated and operated via keyboard controls, with clear focus indicators and instructions.
Incorporating these accessibility best practices guarantees that AI-generated line charts are truly accessible, facilitating broader comprehension and engagement from all users.
Summary
In conclusion, mastering how to generate line charts with AI empowers professionals to craft insightful visualizations efficiently and effectively. As AI technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for creating interactive, precise, and aesthetically pleasing charts are expanding, offering valuable advantages for data-driven decision-making and presentation.