Learning how to generate pie charts with AI opens up innovative possibilities for visualizing data efficiently and accurately. Automating the creation of pie charts using artificial intelligence not only saves time but also enhances the clarity of data presentation. By leveraging advanced AI tools and techniques, users can produce insightful visualizations that are easily customizable and dynamically adaptable to changing data sources.
This guide provides an overview of the various AI-powered methods, tools, and workflows involved in creating compelling pie charts, from data preparation to automation and enhancement. Whether you are a data analyst, developer, or business professional, understanding how AI can streamline your visual data representation processes will significantly improve your reporting and analysis capabilities.
Introduction to AI-generated pie charts
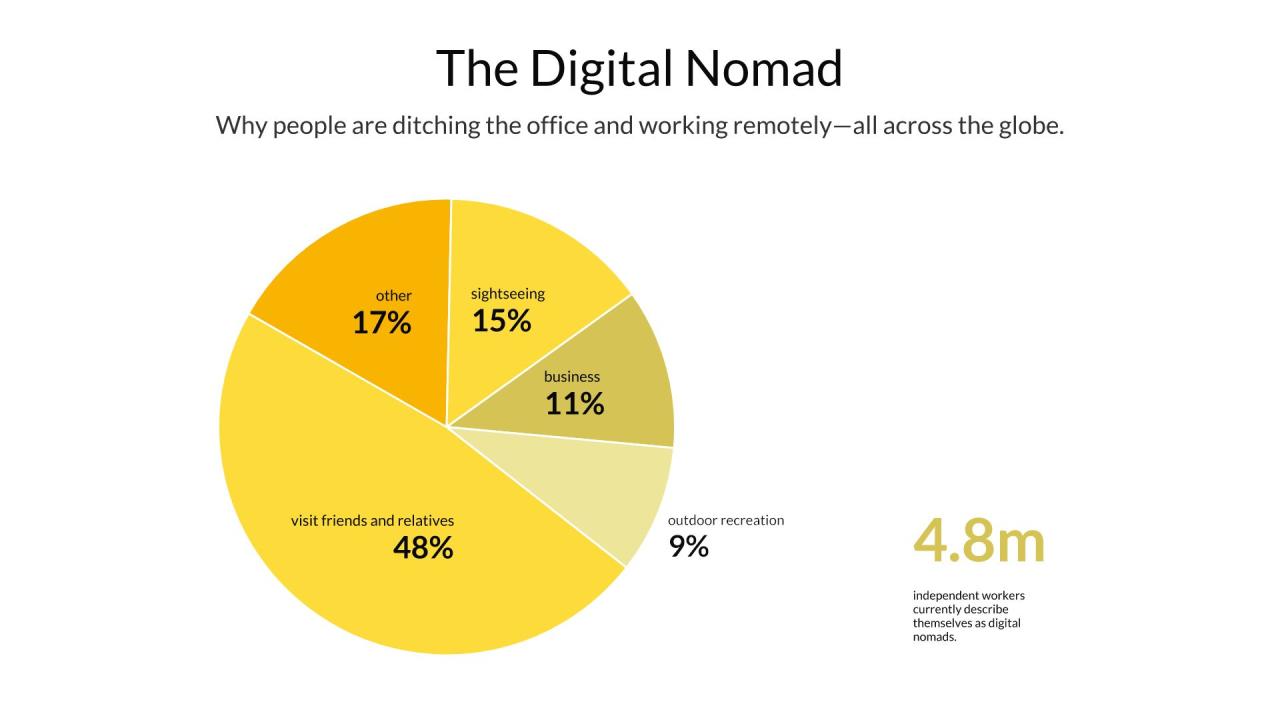
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized the way data visualization is approached, offering innovative solutions for creating compelling and accurate graphical representations. Among these visual tools, pie charts stand out as an intuitive means of displaying proportional data, enabling viewers to quickly grasp relative sizes within a dataset. Utilizing AI to generate pie charts streamlines this process, making it more efficient, precise, and adaptable to complex datasets.
Automating the creation of pie charts through AI tools provides numerous advantages. It reduces the manual effort involved in designing charts, minimizes human error, and accelerates the process of data analysis and reporting. AI-powered platforms can analyze raw data, identify key segments, and produce visually appealing charts that adhere to best practices in data visualization. This automation not only saves time but also enhances consistency across reports and dashboards.
AI methods used for visual data representation
Various artificial intelligence techniques underpin the generation of pie charts, each contributing to different aspects of data processing and visualization. These methods enable AI systems to interpret, analyze, and visually present data efficiently and accurately.
| Method | Description | Application in Pie Chart Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Utilizes algorithms that learn from data patterns to make predictions or classifications. | Automatically categorizes data segments, determines their proportions, and suggests optimal visual layouts for pie charts based on dataset characteristics. |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Enables understanding and processing of textual data. | Processes textual reports or descriptions to extract relevant data points for pie chart creation, especially in automated report generation systems. |
| Data Clustering | Groups similar data points into clusters based on features. | Identifies significant segments within large datasets to be represented as slices in a pie chart, ensuring meaningful visual distinctions. |
| Deep Learning | Employs neural networks with multiple layers to model complex patterns. | Creates advanced visualizations by interpreting high-dimensional data and producing customized pie charts with refined aesthetics and accuracy. |
“AI-driven visualizations enhance the clarity, speed, and consistency of data presentation, empowering users to derive insights more effectively.”
Types of AI Tools for Pie Chart Creation
As artificial intelligence continues to advance, a variety of tools and platforms have emerged to simplify the process of generating pie charts from complex data sets. These tools leverage machine learning algorithms and sophisticated visualization techniques to automate and enhance the creation of categorical data representations, making data analysis more accessible and insightful for users across different industries.
Understanding the diverse landscape of AI-powered pie chart creation tools involves examining popular platforms, software solutions, and open-source resources. Each tool offers unique features, ranging from user-friendly interfaces suitable for novices to advanced capabilities designed for data scientists and developers. Additionally, the way machine learning models are integrated into these tools enables them to analyze, filter, and visually depict categorical data with high accuracy and aesthetic appeal.
Open-source libraries and APIs further democratize access to powerful visualization functionalities, allowing developers to embed AI-driven chart generation directly into custom applications.
Popular AI Platforms and Software for Pie Chart Generation
This section explores some of the most widely used commercial and open-source platforms that facilitate AI-assisted pie chart creation, comparing their features, usability, and suitability for different user needs.
- Tableau: A leading data visualization software that incorporates AI-driven features such as ‘Ask Data’ and ‘Explain Data’, enabling users to generate pie charts interactively through natural language prompts and automated insights. Its integration with machine learning models helps in identifying patterns and suggesting the most compelling visual representations.
- Microsoft Power BI: Offers advanced AI capabilities like ‘Quick Insights’ and ‘Decomposition Tree’ which support the automatic generation of pie charts based on data trends. Power BI’s integration with Azure Machine Learning allows users to enhance visualizations with predictive analytics.
- Google Data Studio: A free, cloud-based platform that can connect with AI-powered data sources and leverage machine learning APIs, simplifying the process of creating dynamic pie charts from large datasets. Its compatibility with Google Cloud AI tools enables scalable and customizable visualizations.
- Charticulator: An open-source tool designed for custom chart creation, including pie charts. While primarily manual, it supports integration with machine learning models via scripting, aiding in automated and data-driven design adjustments.
Machine Learning Models Applied to Visualize Categorical Data
Machine learning models enhance pie chart creation by enabling automated data analysis, categorization, and pattern recognition. These models help in transforming raw, unstructured data into meaningful visual summaries, particularly when dealing with large or complex datasets.
- Clustering Algorithms: Techniques like K-means and hierarchical clustering group similar data points into categories, which can then be visualized as segments in a pie chart. For example, market segmentation based on customer preferences can be visualized to identify dominant segments.
- Classification Models: Algorithms such as decision trees or support vector machines classify data into predefined categories, facilitating the accurate partitioning necessary for pie chart segments. Industries like healthcare utilize classification to categorize patient outcomes or diagnoses visually.
- Dimensionality Reduction: Methods like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) reduce high-dimensional data into key components, which can be mapped into categorical segments and displayed as pie charts to reveal underlying patterns or groupings.
“Machine learning models, when integrated with visualization tools, enable dynamic, insightful, and highly accurate representations of categorical data, transforming raw numbers into compelling visual stories.”
Open-Source Libraries and APIs for AI-Driven Pie Chart Design
Open-source libraries and APIs are vital resources for developers aiming to embed AI-powered pie chart generation into their applications. These tools offer flexibility, customization, and a community-driven ecosystem for continuous improvement and innovation.
- Plotly: A versatile Python and JavaScript library that supports interactive and static pie charts. It integrates with machine learning models to incorporate predictive insights and automate chart adjustments based on data analysis.
- Matplotlib with Scikit-learn: Combining Matplotlib’s visualization capabilities with Scikit-learn’s machine learning algorithms enables users to develop custom workflows for categorizing data and visualizing it as pie charts, suited for research and in-depth analysis.
- D3.js: A powerful JavaScript library for creating dynamic and interactive data visualizations on the web. When coupled with AI APIs like Google Cloud AI or TensorFlow.js, it allows for real-time, AI-driven pie chart updates based on user interactions or incoming data streams.
- Chart.js: An easy-to-use JavaScript library that can be extended with custom AI modules to automatically generate and update pie charts as new data becomes available, supporting real-time analytics dashboards.
These libraries and APIs empower developers to harness machine learning and artificial intelligence for sophisticated, automated pie chart creation, fostering more effective data communication and decision-making processes across diverse fields.
S for Generating Pie Charts with AI
Utilizing AI tools for creating pie charts streamlines the data visualization process, making it faster and more efficient. These tools enable users to input raw data, customize visual aspects, and generate professional-grade charts suitable for reports, presentations, and dashboards with minimal manual effort. Understanding the step-by-step procedures and customization options enhances the ability to leverage AI effectively for data storytelling.
In this section, we focus on the practical workflows involved in inputting data into AI-powered pie chart generators, customizing their appearance, and integrating these visuals into broader reporting frameworks. The emphasis is on delivering clear, actionable guidance that ensures accuracy, aesthetic appeal, and seamless incorporation into professional communication tools.
Inputting Data into AI Tools for Pie Chart Creation
Preparing and entering data correctly into AI tools is fundamental to producing accurate and meaningful pie charts. Here is a systematic approach to ensure smooth data input and effective chart generation:
- Gather Raw Data: Collect the relevant data points that represent the segments of your pie chart. This data could originate from spreadsheets, databases, or manual records.
- Organize Data in a Structured Format: Arrange your data in a tabular format, typically with two columns—one for category labels and another for corresponding values. For example:
- Access the AI Tool: Open the AI-based pie chart generator, which may be a web application or integrated within a data analysis platform.
- Input Data: Depending on the tool, you may upload a CSV or Excel file, or manually enter data into designated input fields. Ensure that data is correctly mapped to categories and values to prevent misrepresentations.
- Validate Data Entry: Review the inputted data within the tool to confirm accuracy before proceeding to visualization.
Category | Value
Sales Q1 | 25000
Sales Q2 | 30000
Sales Q3 | 28000
Sales Q4 | 32000
Following these steps ensures that AI tools have correct and well-structured data, forming the foundation for accurate visualization outcomes.
Customizing Visual Features Using AI Options
Once the pie chart is generated, customizing visual features enhances clarity, branding consistency, and aesthetic appeal. AI tools often provide intuitive options to modify colors, labels, and segment emphasis:
- Colors: Select predefined color palettes or input custom hex codes to assign specific colors to segments, aligning with company branding or thematic preferences.
- Labels: Enable or disable labels that display category names and percentage values. AI options often include font adjustments, size, and positioning to improve readability.
- Segments: Highlight or emphasize particular segments by adjusting their size or coloring to draw attention to key data points.
- Legend and Title: Add, remove, or reposition chart titles and legends to ensure the visualization communicates the intended message effectively.
- Advanced Customizations: Some AI tools offer sliders or input fields for fine-tuning transparency, border thickness, or segment separation to improve visual hierarchy.
Modern AI visualization tools typically provide real-time previews of customization changes, enabling users to iteratively refine their charts for maximum impact and clarity.
Integrating AI-Generated Pie Charts into Reports and Dashboards
Effective integration of AI-generated pie charts into reports or dashboards involves seamless embedding and contextualization. The following workflow ensures professional presentation and usability:
- Export the Chart: Save or download the generated pie chart in suitable formats such as PNG, JPEG, SVG, or PDF, depending on the target platform.
- Embed in Documents: Insert the exported image into reports, presentations, or documentation. Ensure the resolution is high enough to preserve clarity in print or digital formats.
- Incorporate into Dashboards: Upload the chart image or generate dynamic embeds if the AI tool supports integration with dashboard platforms like Power BI, Tableau, or custom web apps.
- Add Contextual Elements: Accompany the chart with text, data source references, and key insights to enhance interpretability.
- Maintain Updates: For dashboards that require live data, ensure the AI tool can connect to data sources or automate refreshes to keep visuals current.
When integrated thoughtfully, AI-generated pie charts serve as powerful visual aids that enhance data comprehension and stakeholder communication across various professional contexts.
Automating Pie Chart Updates with AI

Automating updates for pie charts through AI integration enhances data visualization by providing real-time, accurate representations of evolving datasets. This process ensures that decision-makers always have access to current insights without manual intervention, increasing efficiency and reducing the risk of errors.
By leveraging AI systems connected to live data sources, organizations can create dynamic visualizations that adapt seamlessly to incoming information. The following sections detail methods for establishing these connections, configuring automation workflows, and maintaining the clarity and reliability of automated pie charts.
Connecting AI Systems to Live Data Sources for Dynamic Chart Updates
Establishing a reliable connection between AI tools and live data repositories is fundamental to enabling real-time updates of pie charts. This involves integrating data streams from various sources such as databases, cloud storage, APIs, or streaming services.
Common methods include:
- API Integration: Utilize RESTful APIs or GraphQL endpoints to fetch the latest data at regular intervals. Many AI platforms support API connectors that can be configured to automatically retrieve data from sources like Google Sheets, SQL databases, or third-party analytics platforms.
- Database Connections: Connect directly to SQL or NoSQL databases, enabling the AI system to execute queries that extract updated data sets. This is particularly effective for large-scale enterprise data warehouses.
- Data Streaming Services: Use services like Apache Kafka or MQTT for real-time data feeds, which can be consumed by AI algorithms to update visualizations instantly upon data arrival.
Implementing secure authentication protocols and ensuring data integrity during transmission are crucial for maintaining the accuracy of the update cycle.
Procedures for Setting Triggers and Automation Scripts to Refresh Visualizations
To automate pie chart refreshes, it is essential to define triggers and design scripts that update the visualization when new data arrives or specific conditions are met. Automating this process minimizes manual effort and guarantees timely insights.
Key steps include:
- Defining Triggers: Set triggers based on events such as scheduled intervals (e.g., hourly, daily), data threshold breaches, or new data entries in connected sources. Many automation tools support event-driven workflows that activate upon data updates.
- Creating Automation Scripts: Develop scripts in languages like Python, JavaScript, or specialized automation platforms that fetch the latest data, process it, and update the visualization. For example, a Python script can query a database, generate a new pie chart with libraries like Matplotlib or Plotly, and overwrite the existing visual.
- Integrating with Visualization Platforms: Use APIs or plugins of visualization tools like Tableau, Power BI, or custom dashboards to enable scripted updates. Some platforms support direct scripting within their environment for seamless refreshes.
Combining triggers with scripts ensures that charts remain current without manual prompts, fostering a dynamic data environment that adapts to real-time changes.
Best Practices for Maintaining Accuracy and Readability in Automated Pie Charts
Automated updates must preserve the clarity and correctness of visualizations to be truly effective. Implementing best practices ensures that automated pie charts communicate data accurately and are easy to interpret.
Recommendations include:
- Data Validation: Incorporate validation steps within automation scripts to verify data consistency, completeness, and correctness before visualization. For example, check for missing segments or inconsistent categories that could distort the chart.
- Consistent Formatting: Maintain uniform color schemes, labels, and legends across updates to prevent confusion. Automate label positioning and font sizes to adapt dynamically but stay within readability standards.
- Handling Large or Complex Data: Use aggregation or filtering to simplify complex datasets, preventing cluttered charts. For instance, grouping minor segments into an ‘Others’ category improves legibility.
- Regular Review and Testing: Periodically review automated processes to identify anomalies or inaccuracies. Test scripts with sample data to ensure updates perform as intended without introducing errors.
- Clear Documentation: Document automation workflows, data sources, and validation procedures to facilitate troubleshooting and updates, ensuring long-term accuracy and readability.
By adhering to these practices, organizations can maximize the reliability of automated pie charts, enabling data-driven decisions based on up-to-date and clear visual information.
Enhancing pie charts with AI-driven features

Integrating AI-driven functionalities into pie charts significantly elevates their effectiveness, interactivity, and interpretability. These enhancements enable users to explore data more intuitively, obtain deeper insights, and make more informed decisions. Leveraging AI ensures that pie charts are not just static visuals but dynamic tools tailored to meet diverse analytical needs.
By incorporating intelligent features such as interactive elements, optimized color schemes, and contextual annotations, AI transforms traditional pie charts into powerful analytical instruments. These advancements facilitate clearer data communication, enhance user engagement, and support real-time data analysis in various applications ranging from business reporting to scientific research.
Adding interactive elements such as tooltips and drill-down capabilities
Interactive features are essential for making pie charts more informative and user-friendly. Tooltips provide immediate context by displaying detailed information about each segment when users hover over them, reducing clutter and focusing attention on specific data points. Drill-down capabilities allow users to explore underlying data layers, revealing more granular information without overwhelming the initial visualization.
Implementing these features with AI involves using algorithms that anticipate user interests and dynamically generate relevant details. For example, in a sales data pie chart, hovering over a segment could reveal real-time sales figures, regional breakdowns, or historical trends. Drill-down functionalities might enable clicking on a segment to access detailed transaction records or related charts, facilitating a seamless exploration of complex datasets.
Optimizing color schemes and segment sizes for better clarity
Color schemes and segment proportions critically influence the readability and interpretability of pie charts. AI can assist in selecting color palettes that are accessible to individuals with color vision deficiencies and culturally neutral to avoid misinterpretation. Additionally, AI algorithms analyze data distribution to adjust segment sizes, ensuring that each segment accurately reflects its proportional significance and enhances visual clarity.
Using machine learning, the system can learn from user interactions and preferences, iteratively refining color choices and segment layouts for optimal comprehension. For instance, in a healthcare dataset, AI might emphasize segments representing critical health conditions with distinct, attention-grabbing colors while downplaying less relevant segments, thereby guiding users toward the most important insights.
Generating descriptive annotations and insights alongside pie charts
Annotations and insights provide contextual information that helps users interpret data more effectively. AI-driven systems can automatically generate descriptive labels, summaries, and key takeaways based on the data presented. These insights might highlight trends, anomalies, or comparisons that are crucial for decision-making.
For example, an AI might analyze a pie chart showing market share distribution and generate an annotation stating, ”
Company A holds 45% of the market, experiencing a 5% growth over the previous quarter. This indicates a strong competitive position in the industry.
” Such automated commentary adds value by transforming raw visuals into comprehensive narratives, making complex data accessible to a broader audience.
Examples and Case Studies of AI-Generated Pie Charts

Artificial Intelligence has significantly advanced the creation and analysis of data visualizations, including pie charts, by automating complex processes and enhancing interpretability. Examining real-world instances where AI-generated pie charts have been effectively utilized provides valuable insights into their practical applications and benefits across various industries.
These case studies highlight how AI-driven tools have improved decision-making, optimized resource allocation, and facilitated clearer communication of data insights through sophisticated and dynamic visualizations. The following examples illustrate the diverse contexts in which AI-generated pie charts are making a substantial impact.
Market Research and Consumer Behavior Analysis
In the retail and marketing sectors, AI algorithms analyze large datasets of consumer preferences, purchase history, and demographic information. These insights are translated into pie charts that display market share distributions, product popularity, or customer segmentation.
- Procedure: Data is collected from point-of-sale systems, online surveys, and social media analytics. AI models process this data to identify emerging trends and segment consumers based on buying patterns. The AI then generates pie charts that visually represent the proportion of sales attributed to different product categories or customer demographics.
- Example Output: A retail company uses AI to analyze weekly sales data, producing a pie chart that shows the distribution of sales across five major product categories. The chart dynamically updates as new data arrives, providing real-time insights into changing consumer preferences.
“AI-generated pie charts enable marketers to quickly grasp shifts in customer behavior, leading to more targeted campaigns and inventory adjustments.”
Healthcare Data Visualization
In healthcare, AI systems process patient records, treatment outcomes, and resource utilization data to create pie charts that illustrate the distribution of disease prevalence, treatment success rates, or hospital resource allocation.
- Procedure: Electronic health records (EHRs) are analyzed using AI models that identify common health issues within a specific population. The AI then generates pie charts to visualize the proportion of patients affected by various conditions, aiding clinicians and policymakers in resource planning.
- Sample Output: An AI-powered dashboard displays a pie chart representing the distribution of chronic diseases among patients in a hospital, with segments for diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and others. These visualizations are automatically updated as new patient data is entered.
“AI-generated visualizations facilitate rapid understanding of complex health data, supporting better clinical decisions and policy formulations.”
Financial Analysis and Investment Portfolios
Financial institutions leverage AI to analyze vast amounts of market data, investment performance, and client portfolios. Pie charts created through AI tools depict asset allocation, risk assessment, and market share among competitors.
- Procedure: AI models process historical market data and current financial indicators to recommend optimized portfolio distributions. These recommendations are visualized using pie charts that highlight investment proportions across securities, sectors, or geographical regions.
- Example Output: An AI system generates a pie chart illustrating a diversified investment portfolio, with slices representing stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. The AI continuously refines these visualizations based on market fluctuations and client preferences.
“Automated pie charts in finance enable investors and managers to monitor portfolio diversification in real-time, supporting prompt strategic adjustments.”
These case studies exemplify the versatility and efficiency of AI in producing insightful, accurate, and dynamic pie visualizations across multiple domains. They emphasize how automation and intelligent analysis improve data-driven decisions, leading to more effective strategies and clearer communication of complex information.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, mastering how to generate pie charts with AI empowers users to produce visually appealing and data-rich graphics with minimal effort. By integrating AI-driven tools and automation techniques, creating, updating, and customizing pie charts becomes a seamless part of your data workflow. This approach not only elevates the quality of your visualizations but also facilitates deeper insights and more informed decision-making.