Discovering how to generate flowcharts with AI opens up new possibilities for streamlining process visualization and enhancing communication across various industries. By leveraging advanced technologies, users can transform complex data and textual descriptions into clear, professional diagrams efficiently and accurately.
This guide explores the methods, tools, and best practices for utilizing AI to automate the creation of flowcharts, ensuring effective design, customization, and troubleshooting to optimize your workflow and presentation quality.
Overview of AI-powered flowchart generation
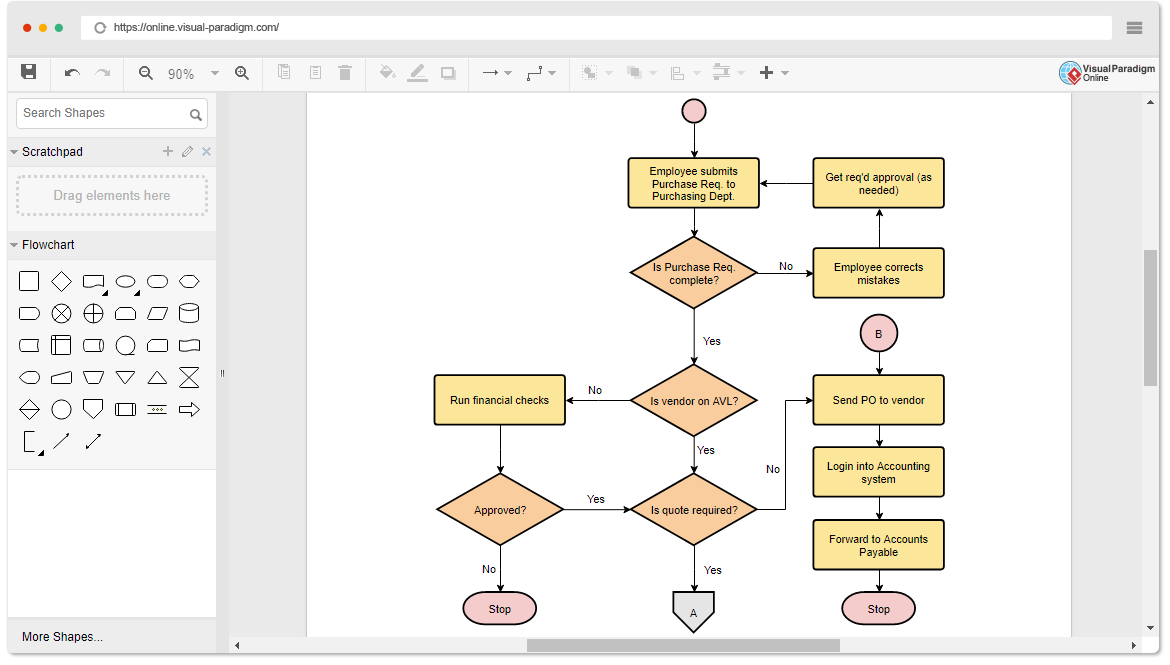
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the way complex data and processes are visualized through automated flowchart creation. By leveraging advanced algorithms and natural language understanding, AI can transform textual descriptions, datasets, or procedural information into clear, structured diagrams with minimal manual effort. This innovation not only accelerates the design process but also enhances accuracy, consistency, and adaptability in workflow visualization.
Utilizing AI for flowchart generation involves inputting unstructured or semi-structured data—such as textual process Artikels or data tables— which AI models interpret to identify key components like steps, decision points, and pathways. These elements are then automatically organized into visual formats, adhering to best practices in diagramming and logical flow. The result is an efficient method for creating detailed, professional diagrams without the need for extensive manual drafting, making it especially valuable in dynamic or complex environments.
Advantages of Automating Flowchart Design with AI
Automating flowchart creation using AI offers numerous benefits that streamline project workflows and improve clarity across various domains. First, it significantly reduces the time required to produce diagrams, allowing teams to focus more on analysis and decision-making rather than manual drawing. Second, AI algorithms ensure consistency in style, symbols, and structure, which enhances readability and standardization across documentation. Third, automation minimizes human error, especially when processing large datasets or intricate processes, leading to more accurate representations.
Another key advantage is the ability to adapt quickly to changes. When process updates or data modifications occur, AI systems can rapidly regenerate flowcharts, maintaining up-to-date visualizations. This dynamic capability is crucial in agile environments where frequent adjustments are common. Additionally, AI-generated flowcharts can leverage machine learning to improve over time, learning from user interactions and feedback to produce increasingly refined diagrams.
Examples of Scenarios Enhancing Workflow Visualization with AI
The application of AI-generated flowcharts spans multiple industries, where complex workflows benefit from swift, precise visual representation. In software development, AI can convert textual specifications or code comments into UML diagrams, aiding developers in understanding system architecture. In manufacturing, process data captured from sensors can be transformed into flowcharts that visualize operational sequences, identifying bottlenecks or inefficiencies. Healthcare providers utilize AI to map patient treatment pathways from electronic health records, enabling clearer communication among multidisciplinary teams.
In business process management, AI tools analyze procedural documentation or emails to automatically generate flowcharts that depict approval workflows, task dependencies, or escalation paths. This not only facilitates process optimization but also supports compliance and training initiatives. The integration of AI in these scenarios enhances clarity, accelerates decision cycles, and promotes a more agile approach to process management.
Methods for generating flowcharts with AI
Transforming textual descriptions into visual flowcharts involves a series of advanced AI-driven processes that interpret, organize, and visualize information efficiently. These methods leverage natural language understanding and diagrammatic rendering to streamline the creation of complex flowcharts, making it accessible for users with varied technical backgrounds. Understanding these methodologies enhances the ability to select appropriate tools and optimize workflows for diagram generation.
Central to AI-based flowchart creation is the conversion of natural language input into structured visual representations. This process typically involves multiple stages, including text preprocessing, semantic analysis, and graphical rendering. Various AI tools and platforms facilitate this transformation by integrating natural language processing (NLP) capabilities with diagram generation engines, providing users with an intuitive experience to produce professional-quality flowcharts from simple descriptions.
Step-by-step process of converting textual descriptions into visual diagrams
- Input Collection: Users provide textual descriptions of the process or system they wish to visualize. This can be a detailed paragraph or a set of instructions outlining steps, decisions, and workflows.
- Natural Language Processing: The AI system employs NLP algorithms to parse the input, identify key entities, actions, and relationships, and interpret the overall structure of the process. Techniques such as tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, and dependency parsing are commonly used at this stage.
- Semantic Analysis and Structuring: The interpreted data is organized into a structured format, often a graph or tree, reflecting the logical flow, decision points, and process sequences. This step ensures that the AI understands the hierarchy and connections between different components.
- Diagram Generation: Using the structured data, the AI tool automatically creates a visual flowchart. It places nodes, connectors, and labels in a manner that accurately represents the interpreted process, adhering to best practices for clarity and readability.
- Refinement and Customization: Users can review the generated diagram, make adjustments if necessary, and customize the appearance or layout through the platform’s interface for enhanced clarity or branding considerations.
Role of natural language processing in interpreting input data
Natural language processing is fundamental to converting free-form textual descriptions into structured, machine-understandable data. It enables the AI to identify essential components such as actions, processes, decision points, and their relationships. By leveraging NLP, AI tools can handle varied input styles, extract relevant information, and minimize manual effort, thus allowing users to rapidly generate accurate flowcharts from simple descriptions.
NLP techniques employed include entity recognition to identify key elements, sentiment and intent analysis to comprehend the purpose of each step, and syntactic analysis to understand sentence structure. These capabilities ensure that the resulting diagrams faithfully represent the input narrative, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
Comparison of AI tools and platforms for flowchart creation
Several AI-powered platforms are designed to facilitate flowchart generation, each with unique features tailored to different user needs. The following table summarizes prominent tools, their core features, and compatibility considerations:
| Tool/Platform | Features | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|
| Lucidchart with AI Integration | Natural language input support, real-time collaboration, customizable templates, AI suggestions for diagram improvement | Web-based, Windows, macOS, Chrome OS, Android, iOS |
| Microsoft Visio with AI Add-ons | Text-to-diagram capabilities via add-ons, integration with Microsoft 365, extensive shape libraries, automation features | Windows, Web (via Office 365), compatible with Azure AI services |
| Creately AI | AI-assisted diagram design, natural language processing, collaborative editing, cloud storage | Web-based, Windows, macOS, Linux (browser compatibility) |
| Draw.io (diagrams.net) with AI plugins | Automated diagram suggestions, text-based input methods, integrations with cloud services like Google Drive and OneDrive | Web-based, Windows, macOS, Linux, Chrome OS |
| Whimsical with AI features | Quick diagram creation from textual descriptions, intuitive interface, team collaboration | Web-based, Windows, macOS, Linux |
These platforms harness NLP and AI-driven algorithms to simplify flowchart creation, enabling users to produce diagrams quickly and accurately from descriptive text. Selection depends on factors such as platform compatibility, integration needs, and specific features like collaboration or custom templates.
Designing Effective Explainings for AI Flowchart Generation
Crafting clear and detailed explanations is essential for guiding AI tools to produce accurate and meaningful flowcharts. Well-designed instructions enable the AI to interpret user intent precisely, resulting in diagrams that meet specific requirements and facilitate easier understanding for end-users. This section explores best practices and strategies for formulating effective explainings that optimize AI flowchart generation.Providing comprehensive and unambiguous instructions is fundamental in ensuring the AI accurately captures the desired structure, style, and content of the flowchart.
Precise explanations serve as a blueprint, reducing the need for multiple iterations and manual corrections. When instructing AI, clarity and specificity can significantly influence the quality and relevance of the generated diagrams.
Techniques for Crafting Precise Instructions
To guide AI effectively, employ techniques that break down complex ideas into clear, manageable directives. Use explicit language to describe each flowchart element, preferred styles, and layout considerations. Incorporate specific details such as the type of flowchart (e.g., process, decision), the number of levels, and visual preferences like color schemes or shapes.Including step-by-step instructions ensures the AI understands the hierarchical relationships and particular formatting expectations.
For example, specify whether decision points should be diamond-shaped or processes rectangular, and clarify the flow direction—top-to-bottom or left-to-right. Consistency in terminology and detailed descriptions reduce ambiguity, leading to more accurate outcomes.
Templates for Explaining AI Flowchart Generation
Using standardized templates for explanations can streamline the communication process and ensure all necessary details are covered uniformly. Templates should Artikel key elements such as flowchart components, styling preferences, and layout configurations. Here is an example template:
| Element | Description | Style/Preferences | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Start/End | Indicates flowchart beginning or termination points | Oval shape, green color | Start |
| Process | Represents an action or operation | Rectangle shape, blue fill | Approve Application |
| Decision | Points requiring a decision | Diamond shape, yellow border | Is Application Complete? |
| Flow Direction | Flow of processes | Top-to-bottom layout, arrows indicating flow | Vertical with arrows pointing downward |
Implementing such templates ensures comprehensive coverage of all necessary instructions, reducing the risk of misinterpretation by the AI.
Examples of Detailed Explaining Structures
Effective explanations benefit from structured articulation that clearly delineates each component of the desired flowchart. Below is an example of a detailed instruction set formatted within a table to specify elements, styles, and layout preferences comprehensively:
| Flowchart Element | Description and Role | Styling & Layout | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Start Point | Denotes the initiation of the process | Oval shape with green fill, labeled ‘Start’ | Position at the top center, with downward flow |
| Decision Node | Critical decision with yes/no branches | Diamond shape, yellow border, labeled ‘Is Data Valid?’ | Branches should diverge left (No) and right (Yes) |
| Process Step | Represents the main operation | Rectangle, light blue background, labeled with specific action | Aligned vertically under decision nodes |
| End Point | Marks process completion | Oval shape with red fill, labeled ‘End’ | Position at the bottom, arrows pointing towards it |
This detailed structure ensures the AI receives explicit guidance on each element, facilitating precise diagram generation.
To enhance output quality, always review and refine your explanations by adding specific details, avoiding ambiguous language, and validating that instructions align with your visual preferences. Clear, consistent, and comprehensive instructions lead to more accurate and visually appealing flowcharts.
Structuring Flowcharts with AI

Effectively organizing and structuring flowcharts with AI tools enhances clarity, simplifies complex processes, and ensures that visual representations accurately reflect operational workflows. Proper procedures for inputting data, selecting styles, and customizing outputs are essential for producing meaningful and professional flowcharts. Additionally, structuring complex processes into simplified visual steps, and integrating decision points and loops effectively, are critical practices that streamline understanding and facilitate decision-making.
Implementing best practices in structuring AI-generated flowcharts involves a systematic approach that combines clear data inputs, thoughtful design choices, and strategic organization of process steps. These practices help users leverage AI capabilities to create intuitive diagrams that are both informative and easy to interpret, regardless of the process complexity.
Procedures for Inputting Data, Selecting Styles, and Customizing Outputs
To maximize the effectiveness of AI-generated flowcharts, users should follow a structured workflow when providing input data, choosing styles, and customizing outputs. This process ensures consistency, clarity, and alignment with organizational standards.
- Input Data Preparation: Collect all relevant process information, including steps, decision points, and dependencies. Structure this data clearly, whether through structured text, tables, or process descriptions, to facilitate accurate AI interpretation.
- Data Upload or Entry: Use the designated input interface of the AI tool to upload files or manually enter process data. Ensure that data is organized logically, with distinct labels for each step or decision point.
- Style Selection: Choose from predefined templates or customize styles based on organizational branding, color schemes, and visual preferences. Use options for node shapes, colors, and line styles to enhance readability.
- Output Customization: Adjust parameters such as layout orientation (horizontal or vertical), spacing, and font sizes to improve visual clarity. Add annotations or notes to specific steps if necessary for additional context.
Organizing Complex Processes into Simplified Visual Steps
Breaking down intricate processes into clear, simplified visual steps improves comprehension and communication. Effective organization involves identifying core components and representing them in a logical sequence.
- Process Decomposition: Divide the overall process into manageable segments or phases, highlighting key activities or decision points within each section.
- Hierarchy and Grouping: Use grouping features to cluster related steps, making it easier to navigate large flowcharts. Hierarchically organize steps from high-level overview to detailed sub-processes.
- Step Consolidation: Combine repetitive or similar steps into a single representative node, reducing clutter and focusing on critical differences.
- Progressive Detailing: Start with a high-level summary and progressively add details in expanded views or secondary diagrams, facilitating focus and clarity.
Incorporating Decision Points and Loops Effectively
Embedding decision points and loops accurately within flowcharts is vital for representing dynamic and conditional workflows. Proper placement and design of these elements help prevent confusion and ensure logical flow.
Decision points should be clearly marked with diamond shapes, with each branch labeled to indicate possible outcomes. Loops should be designed to prevent infinite cycles and clearly indicate the conditions for iteration.
To incorporate decision points and loops effectively:
- Define Decision Criteria: Clearly specify the conditions that lead to different branches or outcomes. Use descriptive labels to denote the decision’s purpose.
- Position Decision Nodes Strategically: Place decision diamonds where choices are made, ensuring they are easily distinguishable and logically positioned within the flow.
- Design Branches Clearly: Use distinct lines or arrows to indicate different paths, and label each to clarify possible outcomes or subsequent steps.
- Implement Loops with Care: Use feedback arrows to connect process steps back to earlier points to represent iterations. Ensure loops are bounded by clear conditions to avoid confusion or infinite cycles.
- Validate Logical Flow: Test the flowchart to confirm that decision outcomes lead to the correct subsequent steps, maintaining process accuracy and readability.
Enhancing flowcharts with descriptive annotations and styling
Visual clarity and contextual understanding are vital components of effective flowcharts. Incorporating descriptive annotations, labels, and thoughtful styling elevates the utility and aesthetic appeal of AI-generated diagrams. By leveraging AI capabilities to add contextual notes and customize visual elements, users can produce more informative and engaging flowcharts that align with branding standards or specific project objectives.
The process of enriching flowcharts with annotations and styling involves integrating text within diagram components, applying color schemes, and customizing visual themes. These enhancements not only improve readability but also facilitate quicker comprehension, especially for complex workflows or technical processes.
Adding notes, labels, and color coding via AI
AI-powered tools can automatically incorporate descriptive notes and labels into flowchart components based on the content or context provided. This automation ensures consistency and saves time, especially when dealing with large or intricate diagrams. Color coding can be assigned to different process types, decision points, or stages, making the flowchart more intuitive.
To add annotations effectively, AI algorithms analyze the diagram’s structure and identify key nodes or pathways requiring clarification. They then generate concise notes or labels, which are seamlessly integrated into the diagram. For example, a decision node might have an AI-generated label such as
“Customer approval required”
, positioned near the decision point for clarity. Color coding can be customized to distinguish between process types, such as using green for completed steps, yellow for ongoing activities, and red for critical issues.
Techniques for customizing visual themes to match branding or purpose
Customizing visual themes enhances brand consistency and reinforces the diagram’s purpose. AI tools often provide options for selecting color palettes, font styles, and shapes that align with organizational branding or specific project requirements. Utilizing these features ensures cohesive visual communication across all diagrams.
Designers can employ predefined themes or create custom themes by specifying color codes, font preferences, and shape styles within the AI interface. For instance, a corporate flowchart can adopt the company’s official color palette, incorporate the logo into diagram backgrounds, and use font styles consistent with branding guidelines. AI can also suggest theme adjustments based on the diagram’s intent—whether formal, educational, or technical—ensuring the visual presentation aligns with the audience’s expectations.
Integrating text annotations into diagrams with detailed descriptive blocks
Effective annotation integration involves strategically placing notes and labels within the flowchart to enhance understanding without cluttering the visual. AI-assisted methods allow for automatic placement of text blocks, ensuring clarity and readability.
Annotations can be embedded directly within diagram nodes as labels or added as adjacent descriptive blocks linked to specific process steps. For example, a process node representing a data processing step might include an annotation such as
“Data validation performed to ensure accuracy”
. Descriptive blocks can also include guidelines, warnings, or additional context, formatted in a way that visually distinguishes them from primary diagram elements—using borders, background shading, or icons.
AI tools often provide customization options for these annotations, including font size, color, and placement, ensuring they complement the overall visual style and do not impede diagram flow. Properly integrated annotations serve as quick-reference points, reducing the need for external explanations and improving overall comprehension.
Styling options within descriptive blocks for visual differentiation
Stylish and functional descriptive blocks can significantly improve flowchart readability and aesthetic appeal. These blocks can be styled using various options to highlight important information or differentiate between different types of annotations.
Common styling options include:
- Background Colors: Using contrasting or thematic background colors to make annotations stand out or blend with overall theme.
- Borders and Shadows: Adding borders or shadow effects to create visual separation and depth.
- Font Styles and Sizes: Varying font weight, style, or size to emphasize particular notes or categorize annotations.
- Icons and Symbols: Incorporating relevant icons (e.g., warning signs, info symbols) to quickly convey the nature of the annotation.
- Shape Variations: Utilizing different shapes such as rounded rectangles, ovals, or callouts to distinguish types of annotations or importance levels.
For example, a critical warning annotation might be styled with a red background, bold font, and an exclamation icon, making it immediately recognizable. Conversely, informational notes could be presented in softer colors with plain fonts. AI tools often include templates or style presets to streamline this process, enabling users to apply consistent styling across multiple annotations within a diagram.
Examples of AI-generated flowcharts in various industries
Artificial Intelligence has revolutionized the way organizations visualize complex processes across diverse sectors. By automatically interpreting vast amounts of industry-specific data, AI-powered tools can generate detailed, accurate, and dynamic flowcharts tailored to the unique workflows of each field. These visual representations enhance clarity, streamline communication, and facilitate better decision-making. Below, we explore several illustrative case studies that demonstrate the application of AI-generated flowcharts in sectors such as software development, healthcare, and manufacturing.
These examples highlight how AI interprets industry-specific data to produce relevant flow diagrams and the significant impact they have on project planning, operational efficiency, and interdepartmental communication.
AI-generated flowcharts in software development
In the software industry, AI-driven flowchart tools analyze codebases, development workflows, and project requirements to generate visual representations of system architecture, data flow, and process sequences. These flowcharts aid developers and project managers by providing an instant overview of complex algorithms and integration points.
- Interpretation of Code and Logic: AI tools parse programming languages and identify logical structures, converting them into flowcharts that illustrate decision trees, loops, and function calls. This process reduces manual documentation efforts and enhances understanding among team members.
- Automated Workflow Visualization: When integrating new modules or features, AI systems analyze dependency graphs and generate diagrams that reflect current development pipelines. This supports agile planning and helps identify potential bottlenecks early.
- Benefits: Faster onboarding of new developers, improved code review processes, and clearer communication of system architecture to non-technical stakeholders.
AI-generated flowcharts in healthcare
The healthcare industry leverages AI to create flowcharts that map patient treatment pathways, diagnostic procedures, and administrative processes. These diagrams facilitate clinical decision support, streamline patient management, and optimize resource allocation.
- Interpreting Clinical Data: AI analyzes electronic health records (EHRs), lab results, and imaging reports to construct flowcharts that depict diagnostic workflows and treatment protocols based on patient-specific data.
- Streamlining Diagnostic Processes: AI-generated diagrams can visualize decision trees used by clinicians to determine next steps, such as laboratory tests, imaging, or specialist referrals, thereby reducing diagnostic delays.
- Benefits: Enhanced clarity in complex treatment plans, improved communication among multidisciplinary teams, and data-driven optimization of clinical pathways.
AI-generated flowcharts in manufacturing
Manufacturing companies utilize AI to model production workflows, quality control processes, and supply chain logistics. These flowcharts enable real-time monitoring, identify inefficiencies, and facilitate continuous process improvement.
- Analyzing Operational Data: AI systems process sensor data, machine logs, and production schedules to produce flow diagrams illustrating process sequences, machine states, and material flows.
- Optimizing Production Lines: AI-generated flowcharts highlight bottlenecks, redundant steps, and potential points of failure, providing actionable insights for process reengineering.
- Benefits: Increased operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved product quality through precise visualization of complex manufacturing workflows.
These case studies exemplify how AI-generated flowcharts serve as powerful tools across industries, transforming raw data into meaningful visual representations that support strategic planning, operational excellence, and effective communication among teams and stakeholders.
Troubleshooting common issues in AI flowchart creation
Creating accurate and effective AI-generated flowcharts can sometimes present challenges, especially when initial outputs do not meet expectations due to technical or interpretative errors. Addressing these issues systematically ensures that the final diagrams are clear, correct, and useful for decision-making or process visualization. Recognizing typical problems and adopting structured troubleshooting methods are essential skills for users leveraging AI tools for flowchart generation.AI flowchart creation can encounter errors stemming from misinterpretation of input data, formatting inconsistencies, or limitations in the AI model’s understanding of complex processes.
These issues may manifest as incorrect node connections, missing steps, or confusing layout arrangements. Proper diagnosis involves analyzing the input prompts, reviewing the generated output, and understanding the underlying AI model’s behavior.
Common errors in AI flowchart generation
It is important to be aware of typical errors that can occur during AI-assisted flowchart creation to facilitate prompt correction and optimization. These errors often impact the clarity, accuracy, and usability of the diagrams.
- Misinterpretation of input instructions: When prompts are vague or ambiguous, the AI may generate flowcharts that do not align with the intended process, leading to inaccuracies or incomplete diagrams.
- Formatting inconsistencies: Incorrect or incompatible input formatting, such as inconsistent use of s or structure, can cause the AI to misread the data, resulting in misplaced nodes or improper connections.
- Layout and spacing issues: Overlapping elements, disproportionate node sizes, or poorly organized layouts reduce the readability of the flowchart and can obscure key process steps.
- Content inaccuracies: Errors in the generated content, such as incorrect decision paths or missing steps, often stem from insufficient or incorrect input data.
Steps to correct and optimize AI outputs
Effective troubleshooting involves clear, repeatable steps that help refine the AI-generated diagrams, ensuring they accurately reflect the intended processes.
- Review and clarify input data or prompts: Ensure the instructions are explicit, well-structured, and free of ambiguity. For example, specify the start and end points, decision criteria, and sequence explicitly to guide the AI.
- Validate the initial output: Examine the generated flowchart for discrepancies, such as missing steps, illogical connections, or layout issues. Mark the areas requiring correction.
- Refine input prompts and re-generate: Adjust the prompts based on the observed issues, emphasizing clarity or adding missing details, then re-submit for processing.
- Manually edit or annotate the AI output: Use diagram editing tools to correct layout issues, add missing annotations, or rearrange nodes for improved clarity.
- Implement automation checks: Integrate validation scripts or rules that flag common errors, such as unconnected nodes or inconsistent decision paths.
Diagnosing and resolving layout or content inaccuracies
Layout problems and content errors can significantly reduce the effectiveness of AI-generated flowcharts. Diagnosing these issues involves a systematic examination of both the diagram and the input data.
- Layout inaccuracies can be diagnosed by checking for overlapping nodes, disproportionate sizes, or misaligned connections. These are often caused by overly complex or poorly formatted input data.
- Content inaccuracies include incorrect decision paths or missing steps, which require cross-referencing the flowchart against the original process description or data sources.
To resolve these problems:
- Identify the specific misalignments or omissions within the diagram.
- Adjust the input prompts to clarify ambiguous steps or decision logic.
- Use diagram editing tools to manually correct node positions and connections, ensuring a logical flow.
- Consult domain experts or process owners to verify the accuracy of the diagram content, updating prompts accordingly.
Checklist for ensuring clarity and completeness in AI-generated diagrams
A comprehensive checklist helps maintain the quality and utility of flowcharts produced with AI assistance:
- Clear and explicit input instructions: Confirm that prompts specify process boundaries, decision points, and flow directions explicitly.
- Consistent formatting: Use standardized terminology, symbols, and structure within the input data to facilitate correct interpretation.
- Validation of initial output: Review the diagram thoroughly for missing steps, illogical connections, or layout issues.
- Alignment with original process: Cross-verify the flowchart against the actual process or data source to ensure completeness.
- Manual adjustments: Use editing tools to correct layout issues, improve readability, and add annotations or styling as needed.
- Feedback incorporation: Revise prompts or inputs based on observed issues to improve subsequent generations.
- Documentation of issues and corrections: Keep records of common errors encountered and their solutions to streamline troubleshooting in future projects.
Ensuring these elements are addressed systematically can significantly improve the accuracy, clarity, and usability of AI-generated flowcharts, making them valuable tools for process analysis and presentation.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, mastering how to generate flowcharts with AI empowers users to produce precise and visually appealing diagrams with minimal effort. Embracing these innovative techniques can significantly improve planning, decision-making, and communication within any professional setting, making your process visualization more effective than ever before.